Sponsor: National Science Foundation and United Technologies Corporation
Graduate Students: S.Chaudhuri (Ph.D. Candidate), M. Andel (M.S. Candidate), Alper Ata (M.S. in ME, 2003), Andres Chaparro (M.S. in ME, 2004)
Project Summary
This project concerns characterization of flame blow-off for lean premixed flames under upstream time-periodic velocity oscillations and spatial mixture gradients. Experiments are carried out in two geometries. First involves an axisymmetric configuration where premixed flames are stabilized at the nozzle exit on a bluff-body flame holder attached to a center sting. Second experimental configuration is that of a rectangular duct where a V-gutter flanme holder spans the duct width. In each case, flame blow-off conditions are experimentally characterized for a range of mixture approach velocities (5 to 20 m/s), upstream velocity oscillation amplitude and frequency as well as the radial gradient of mixture equivalence ratio. The employed flow diagnostics include Rayleigh scattering for mixture characterization, CH* flame emission, particle image velocimetry and high speed flame imaging.

Experimental set-up for the blow-off studies
Variation of blow-off equivalence ratio with excitation frequency for different bluff body shapes
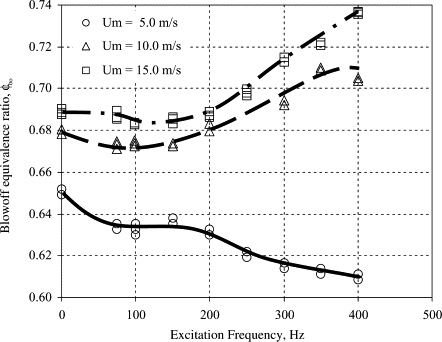
Disk shaped bluff body
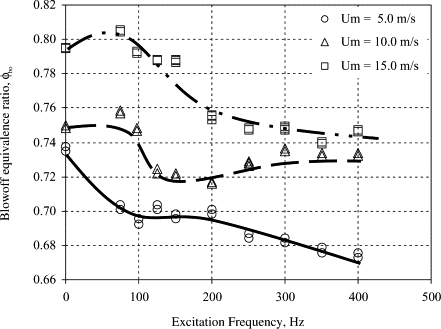
Rod shaped bluff body

Premixed conical flame with higher fuel concentration in the inner nozzle
Time variation of velocity and photomultiplier voltages at 100 Hz
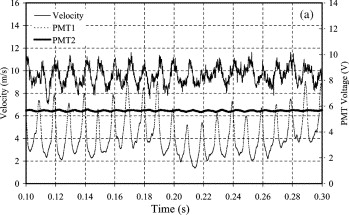
Coherence between velocity and photomultiplier signals

PMT1: masked at 500 mm height above the flame holder; PMT2: unmasked viewing the whole flame.
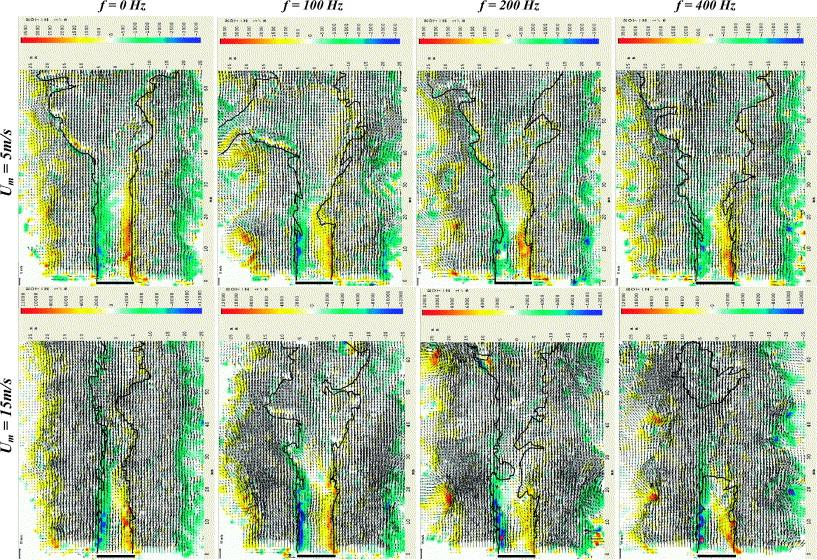
Instantaneous velocity field and vorticity maps for the rod-shaped bluff body before blowoff at flow velocities of 5 and 15 m/s and excitation frequencies of 0, 100, 200, and 400 Hz. Vorticity scale: top row, ±3500 1/s; bottom row, ±12,000 1/s.
Flame images obtained by reversing the Mie scattering images obtained during the PIV experiments for the 10-mm-diameter rod-shaped bluff-body flame holder (arrows show the length scale l=Um/f).